Act on the national cybersecurity certification system – for whom cybersecurity certificates will be needed.
Publication date: September 16, 2025
Cybersecurity certifications are designed for IT professionals, including system and network administrators, security specialists, engineers, and those aspiring to these roles, to validate their knowledge and practical skills in protecting against digital threats. The certification also covers ICT products, services, and processes, and aims to inform consumers about the level of digital security and support Polish companies in European markets.
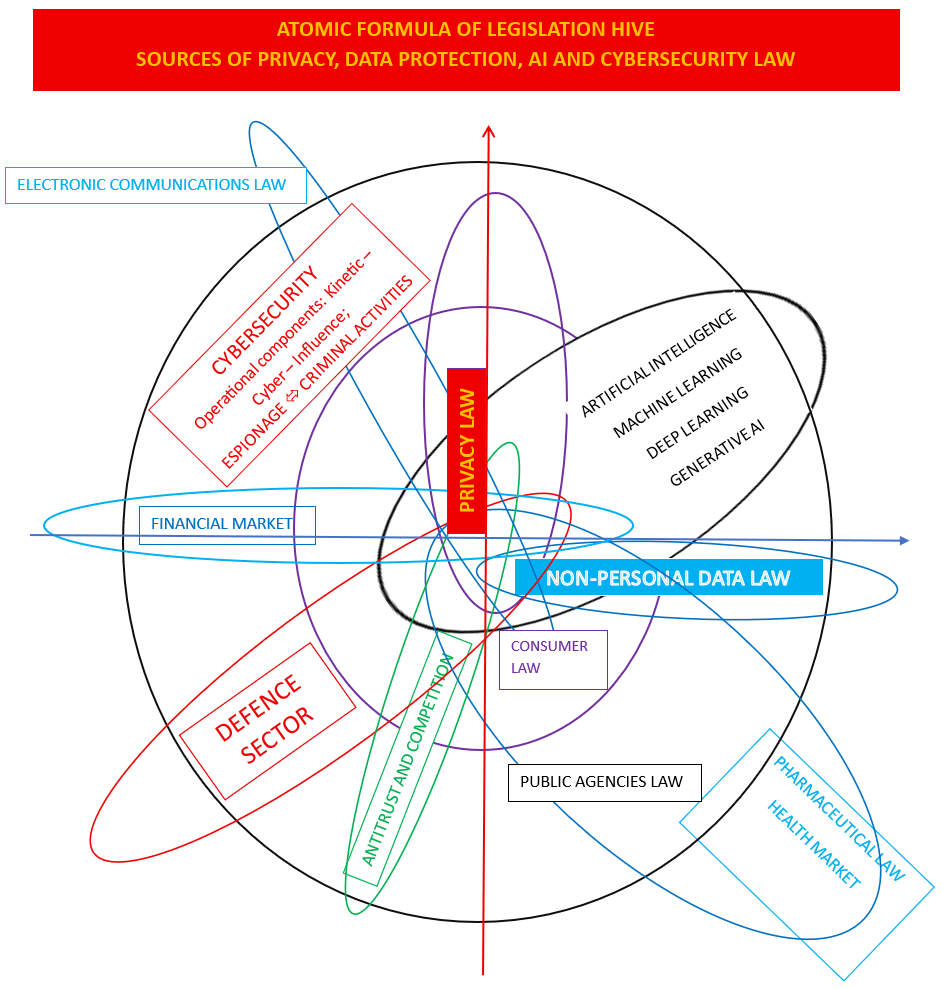
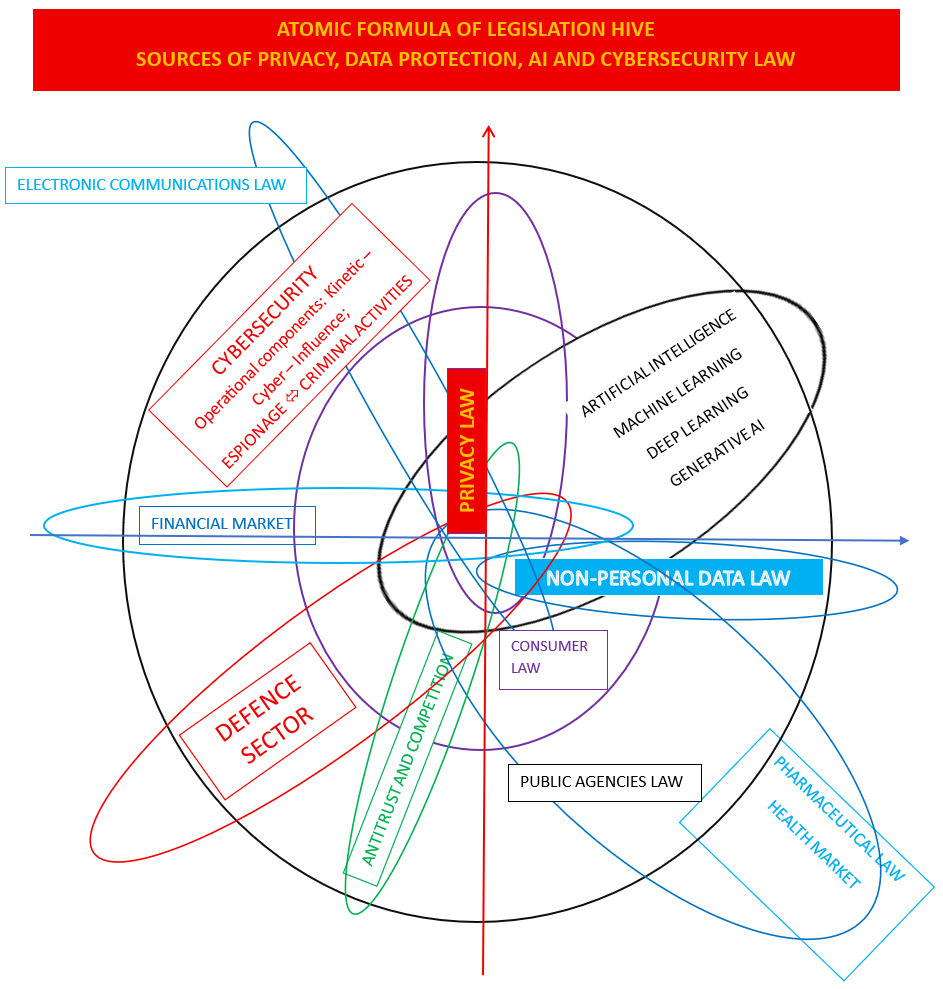
PRIVACY, DATA PROTECTION, AI AND CYBERSECURITY – LAW MAP
Publication date: September 15, 2025
The phenomenon of dispersion of data law sources
Data law is no longer just about GDPR. The European Union’s legislative trend of incorporating data law regulations into comprehensive sectoral regulations: healthcare, financial markets, corporate stock market law, the defense industry, electronic communications, and the phenomenon of fair competition in trade, is resulting in a significant fragmentation of legal sources, the core subject of which is “DATA AND DATA PROTECTION